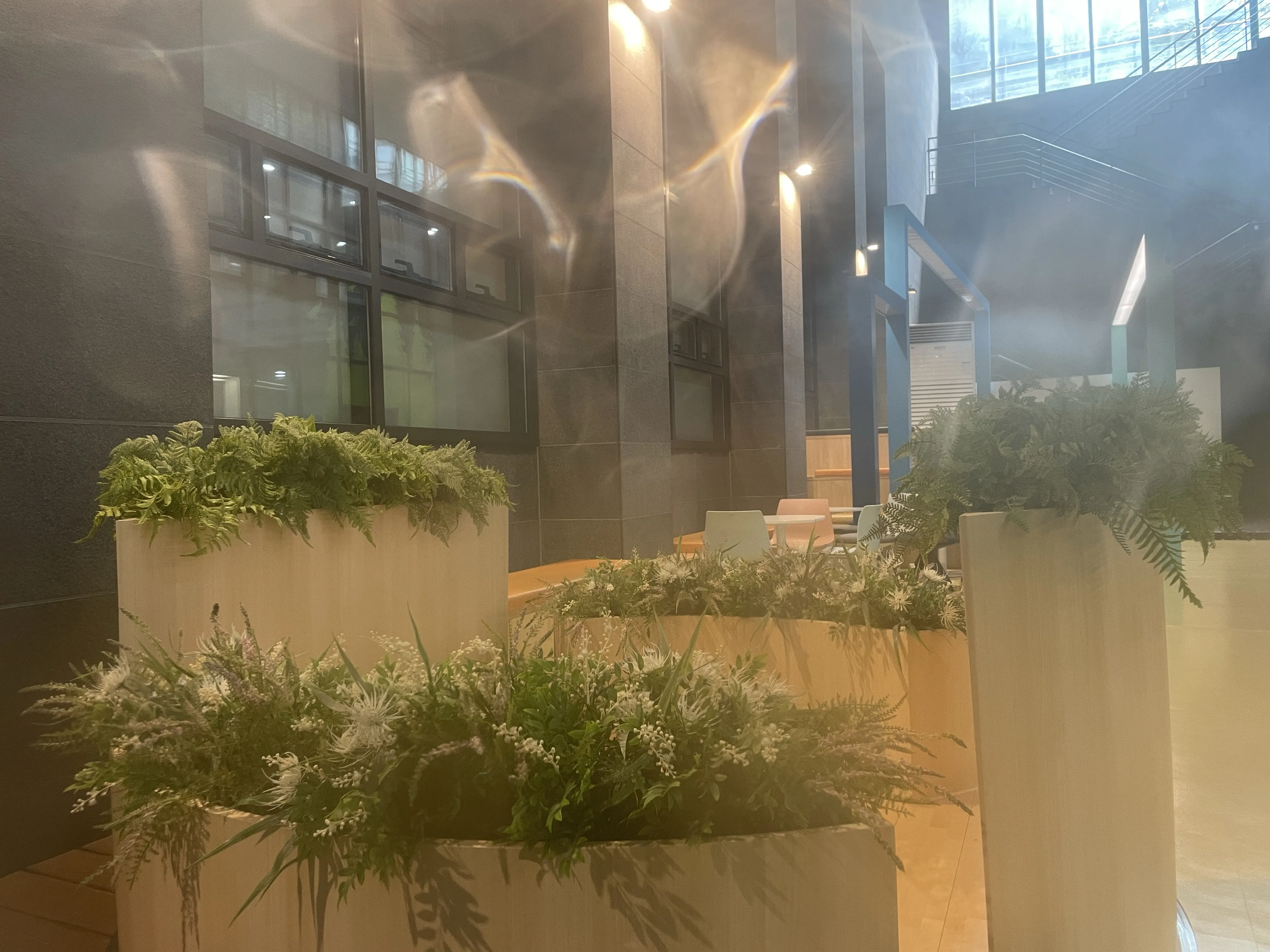
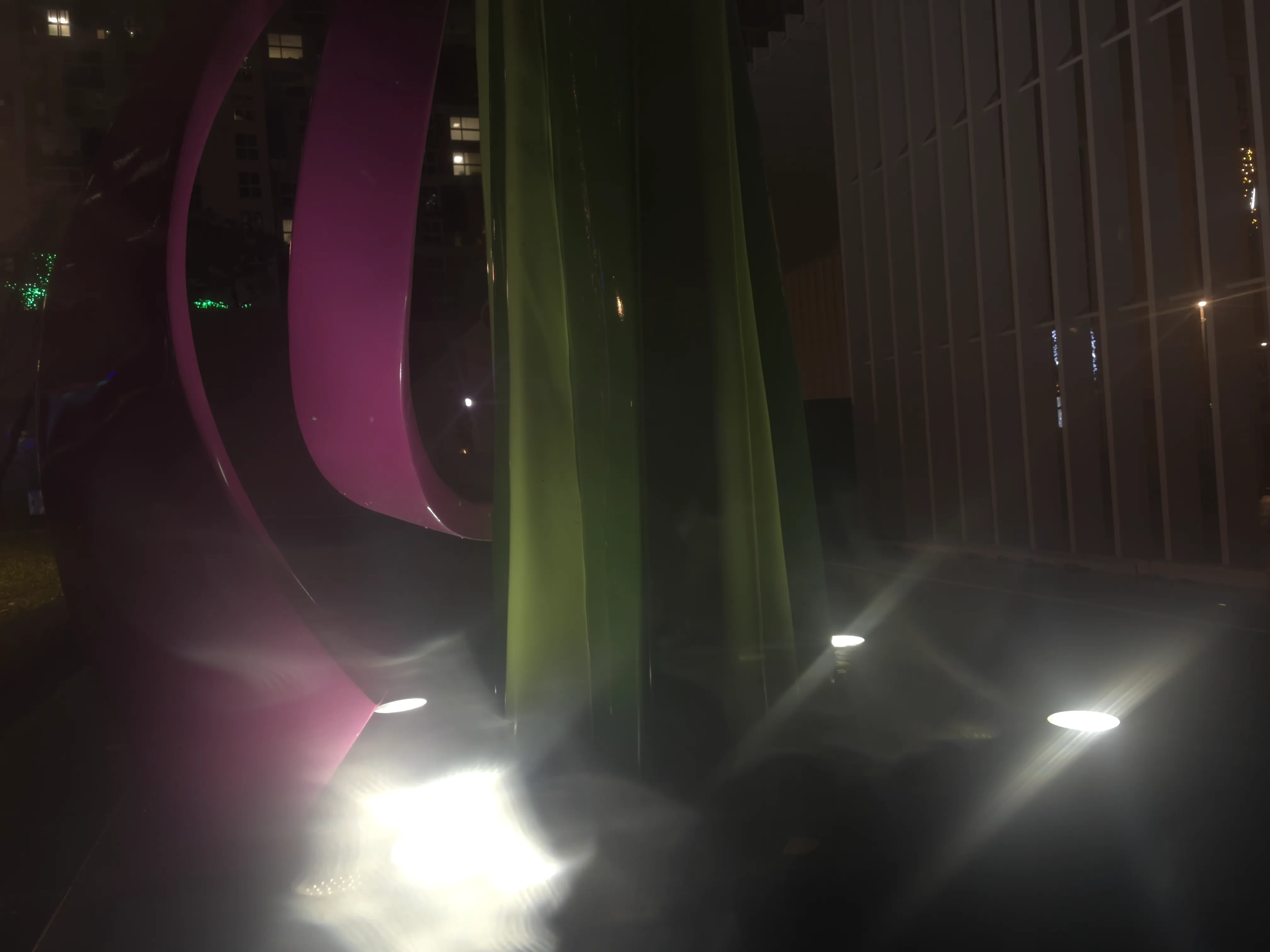
























Abstract
Smartphone cameras are ubiquitous in daily life, yet their performance can be severely impacted by dirty lenses, leading to degraded image quality. This issue is often overlooked in image restoration research, which assumes ideal or controlled lens conditions. To address this gap, we introduced SIDL (Smartphone Images with Dirty Lenses), a novel dataset designed to restore images captured through contaminated smartphone lenses. SIDL contains diverse real-world images taken under various lighting conditions and environments. These images feature a wide range of lens contaminants, including water drops, fingerprints, and dust. Each contaminated image is paired with a clean reference image, enabling supervised learning approaches for restoration tasks. To evaluate the challenge posed by SIDL, various state-of-the-art restoration models were trained and compared on this dataset. Their performances achieved some level of restoration but did not adequately address the diverse and realistic nature of the lens contaminants in SIDL. This challenge highlights the need for more robust and adaptable image restoration techniques for restoring images with dirty lenses
SIDL Dataset
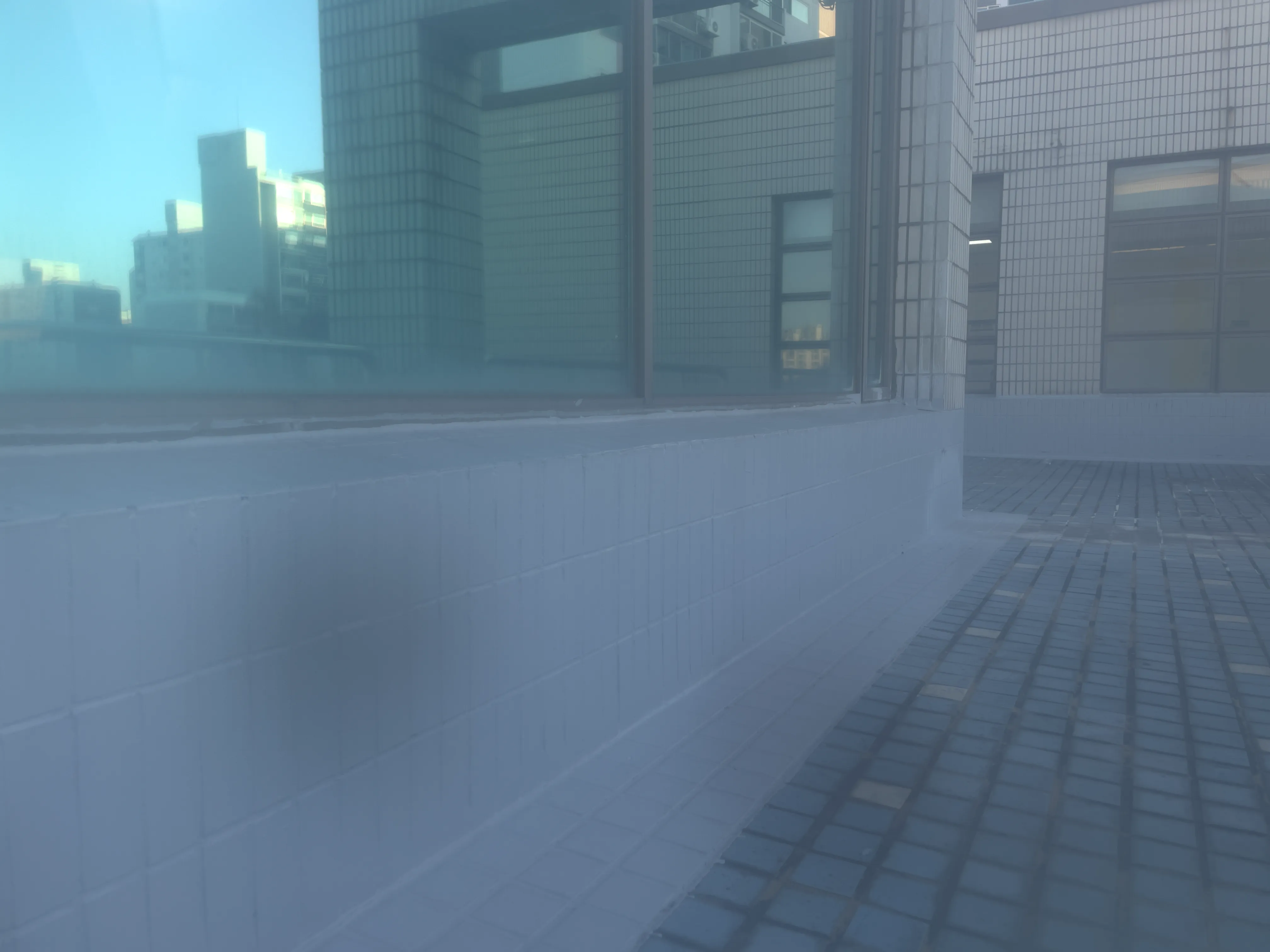
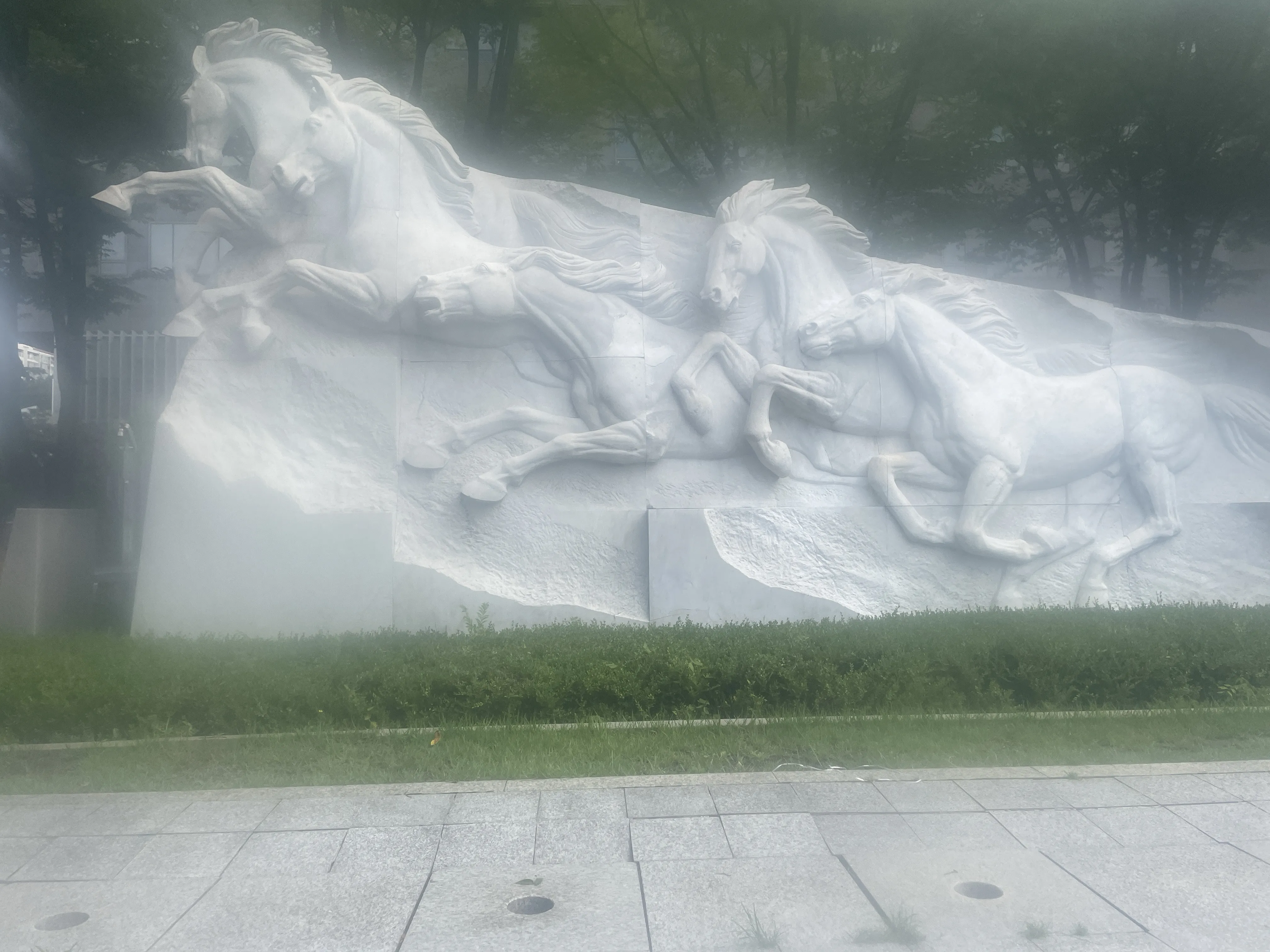
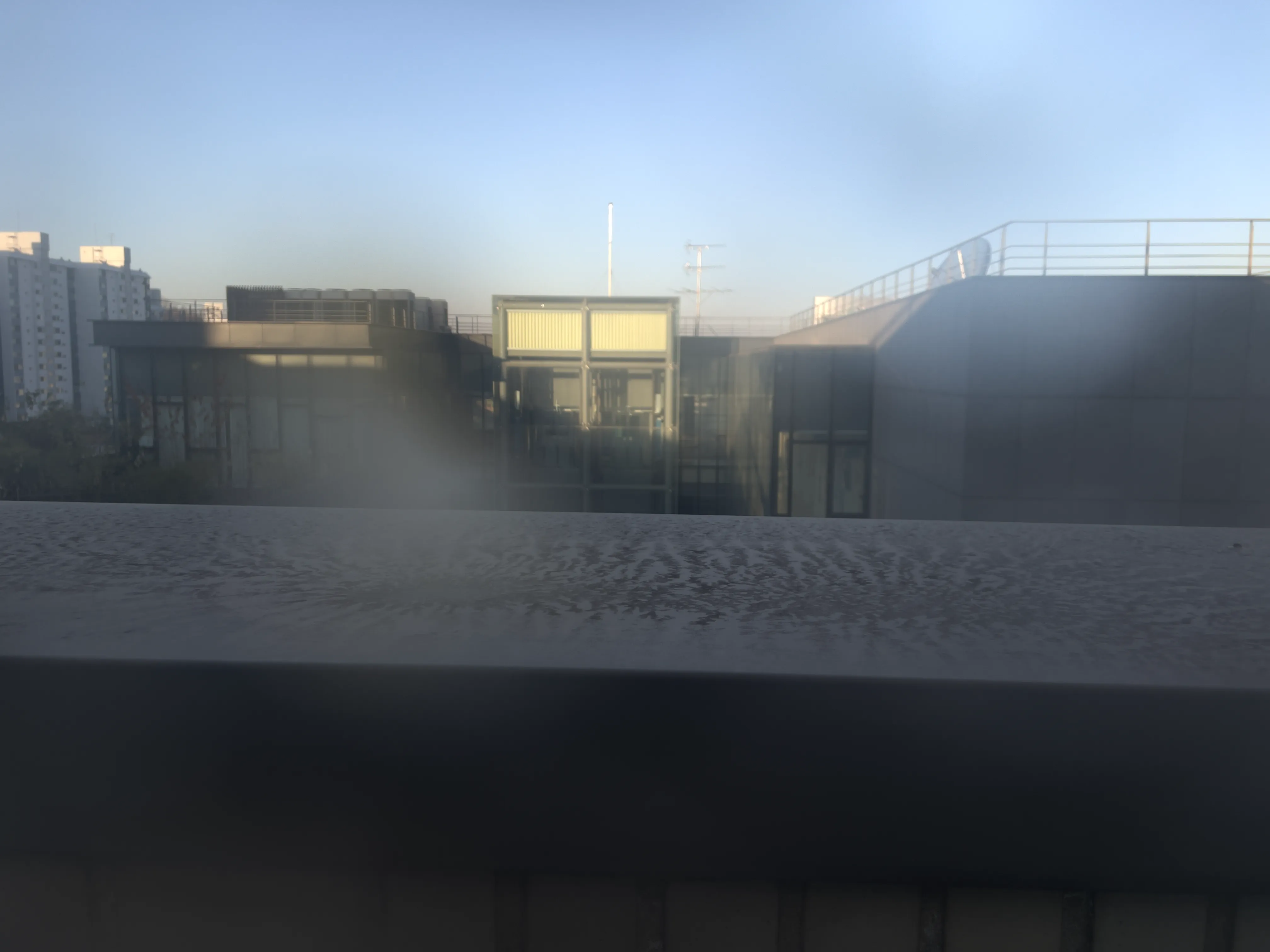
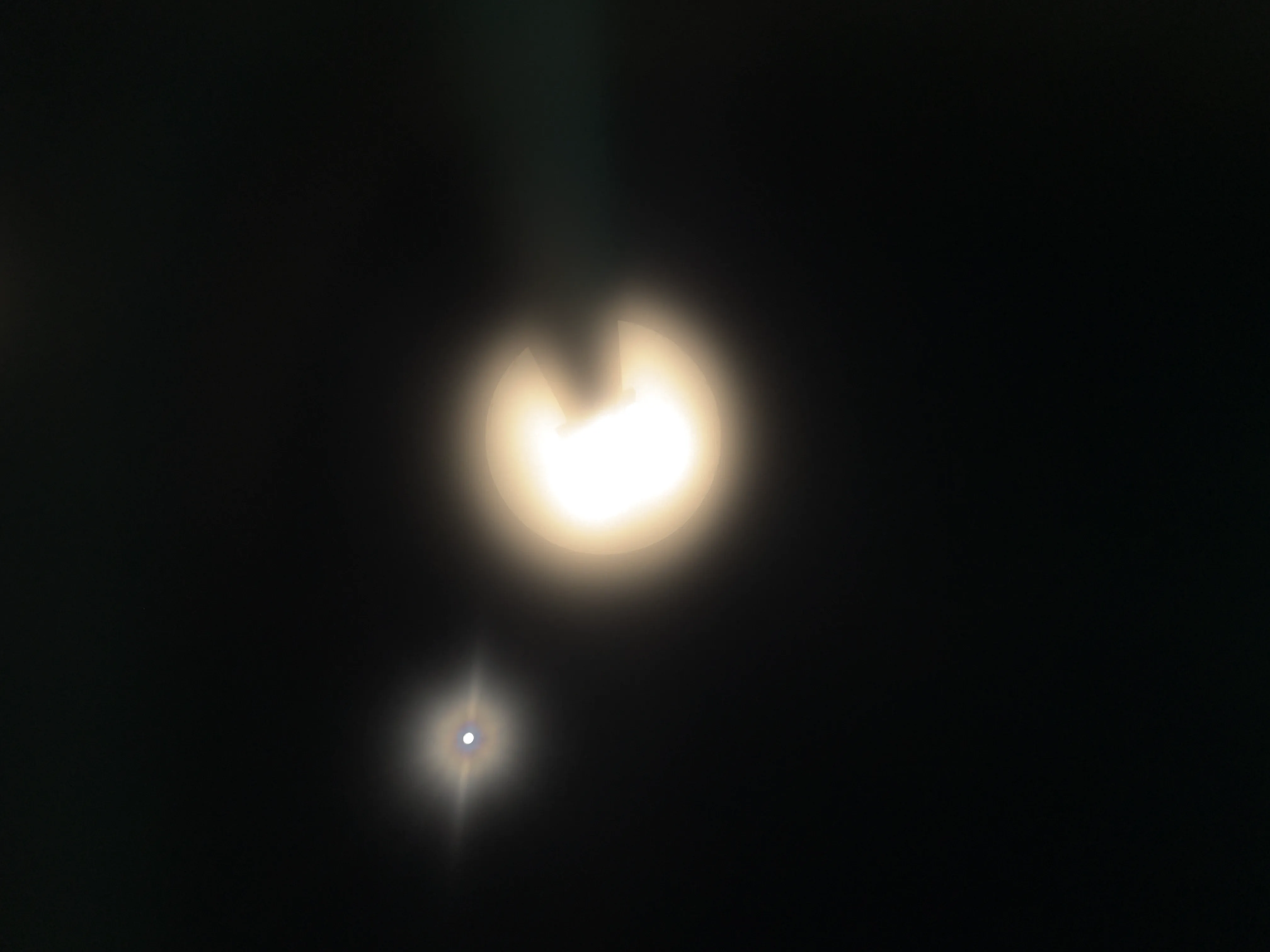
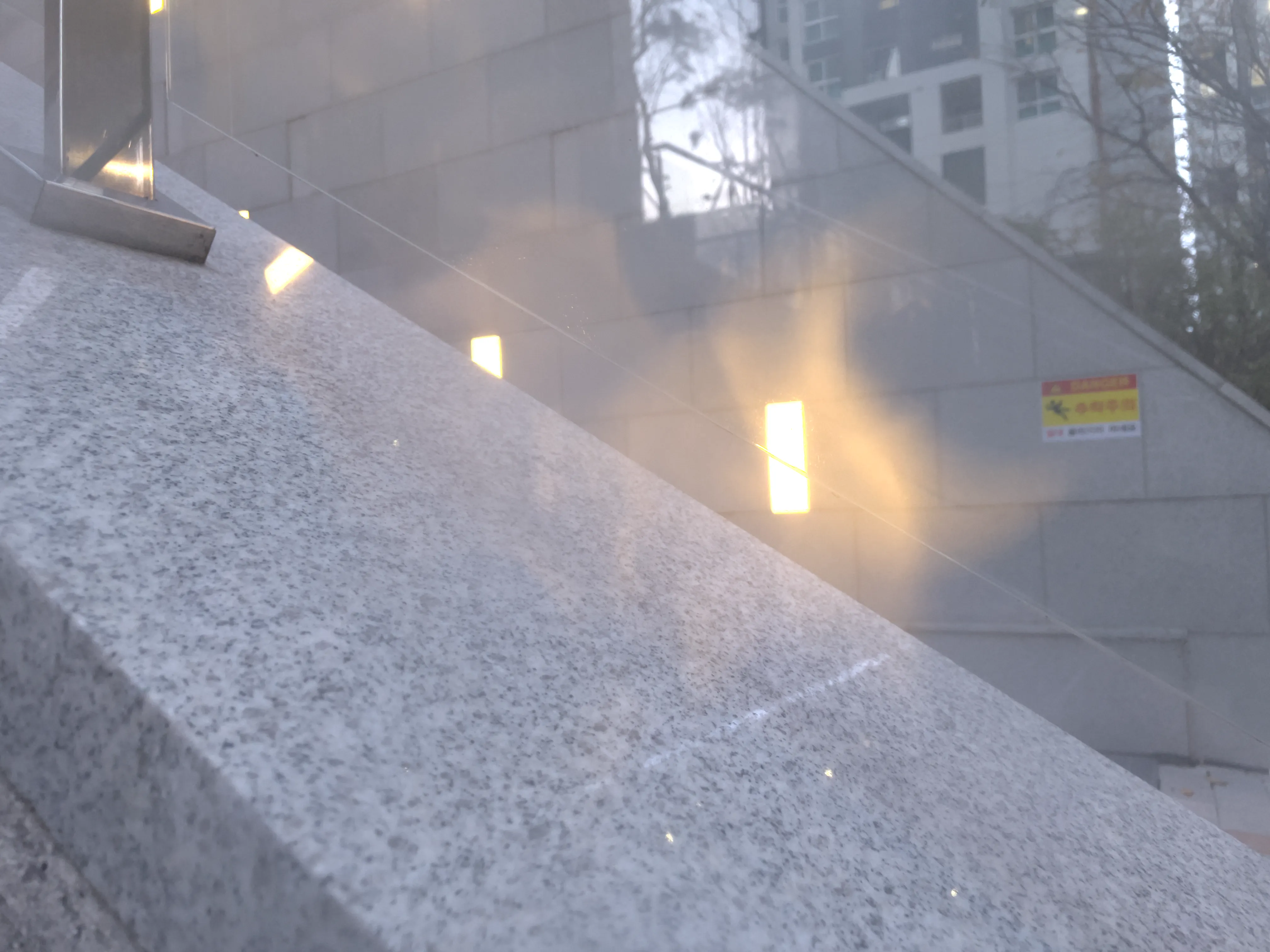
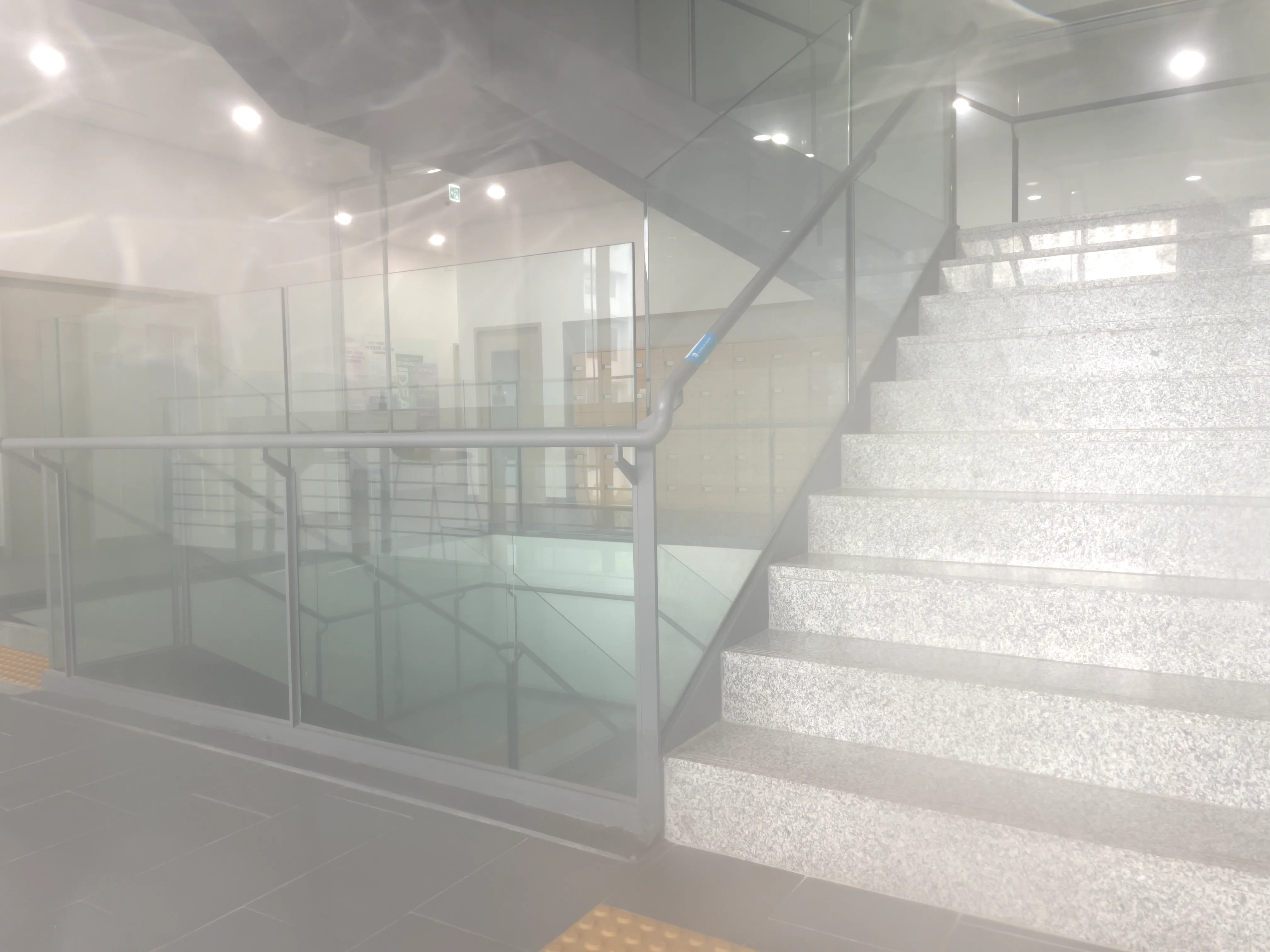
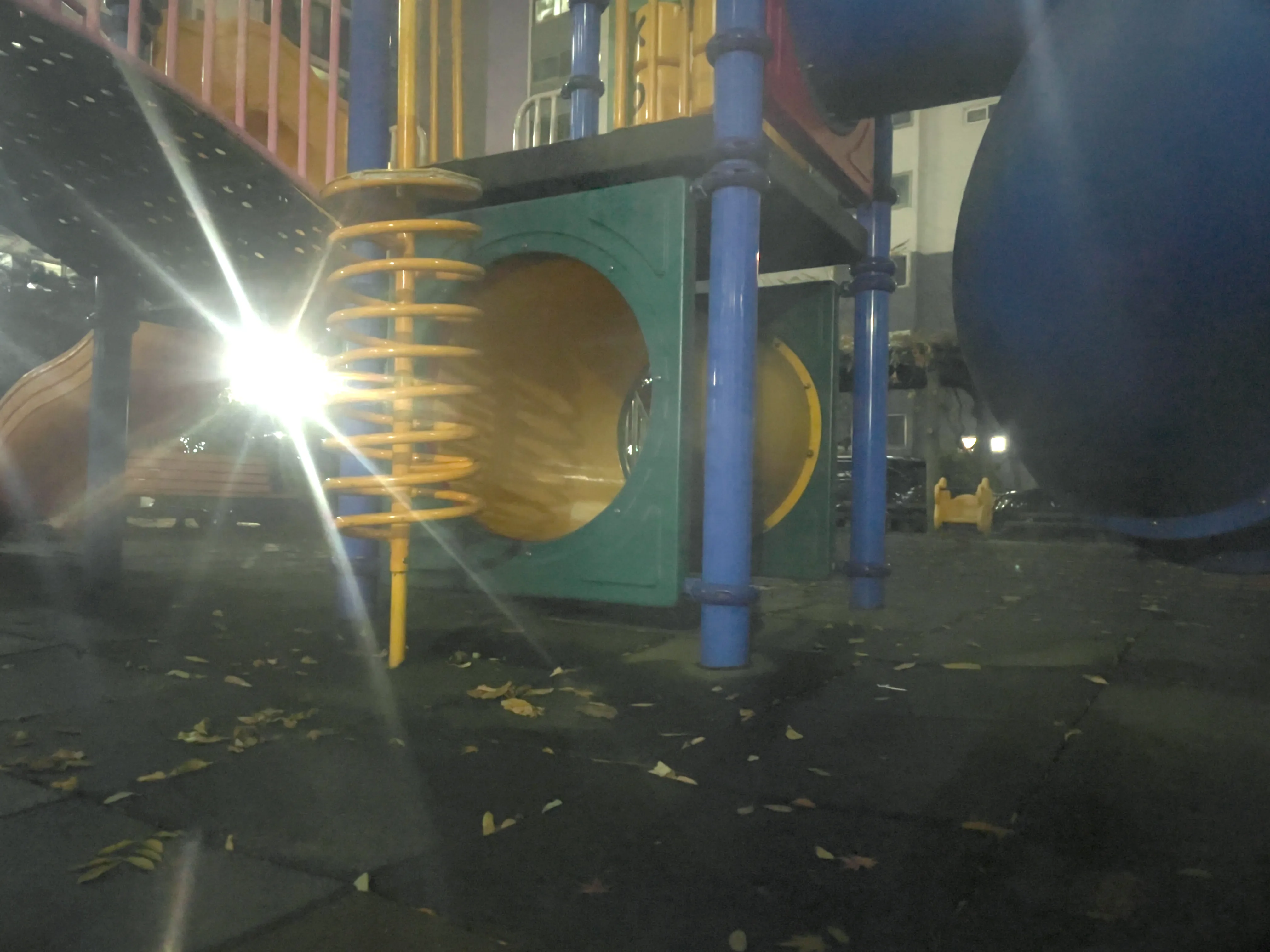
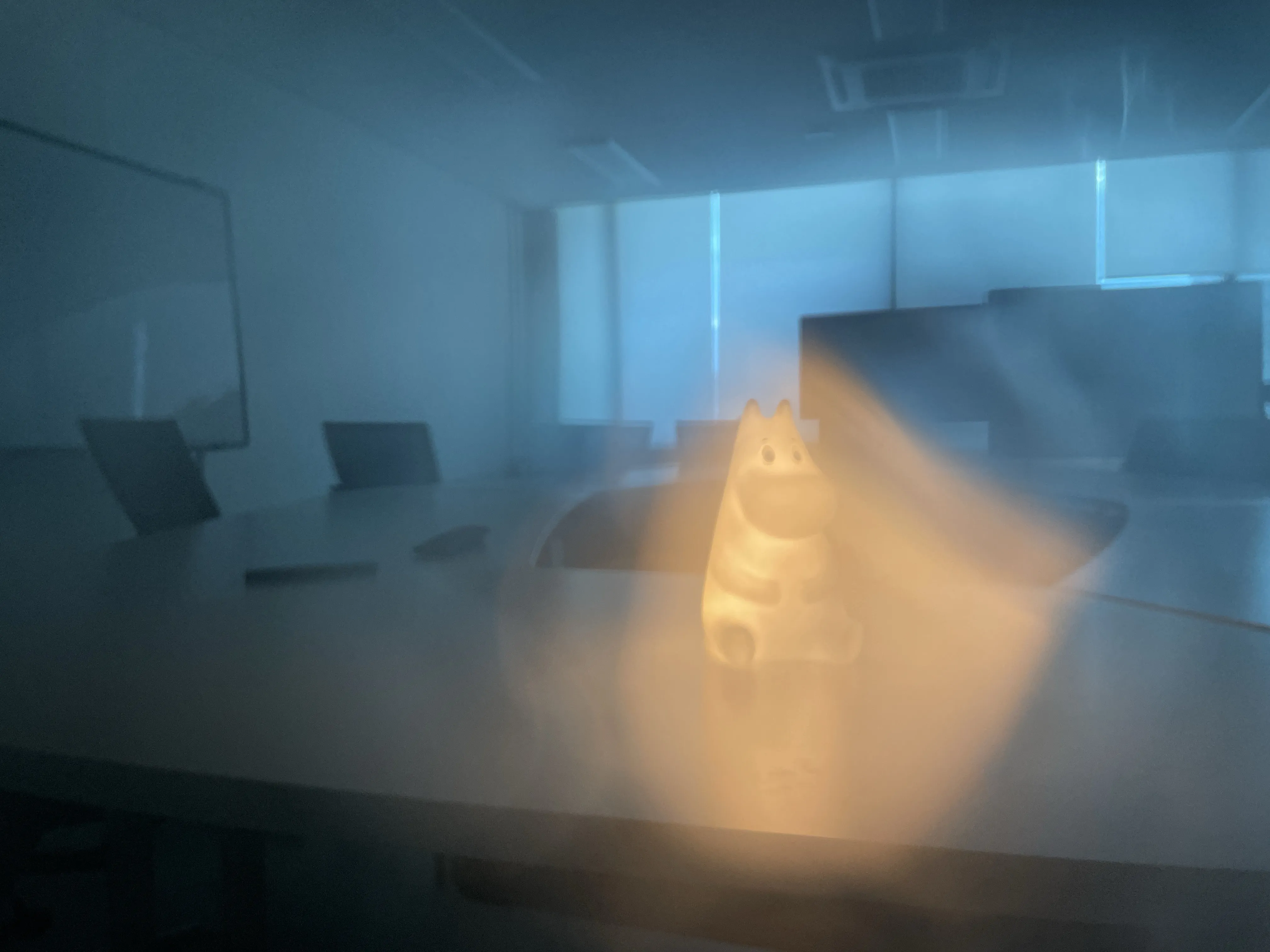
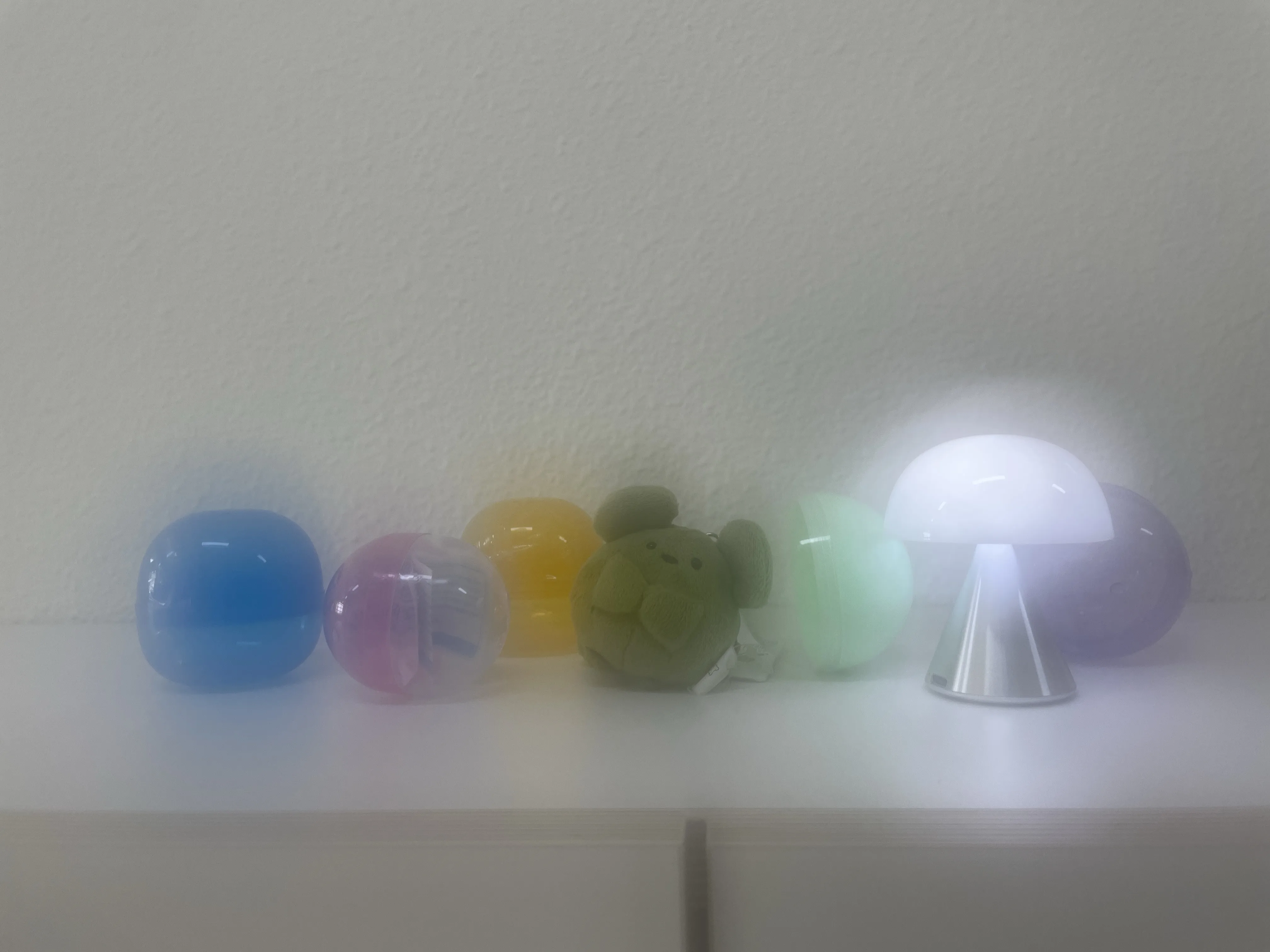
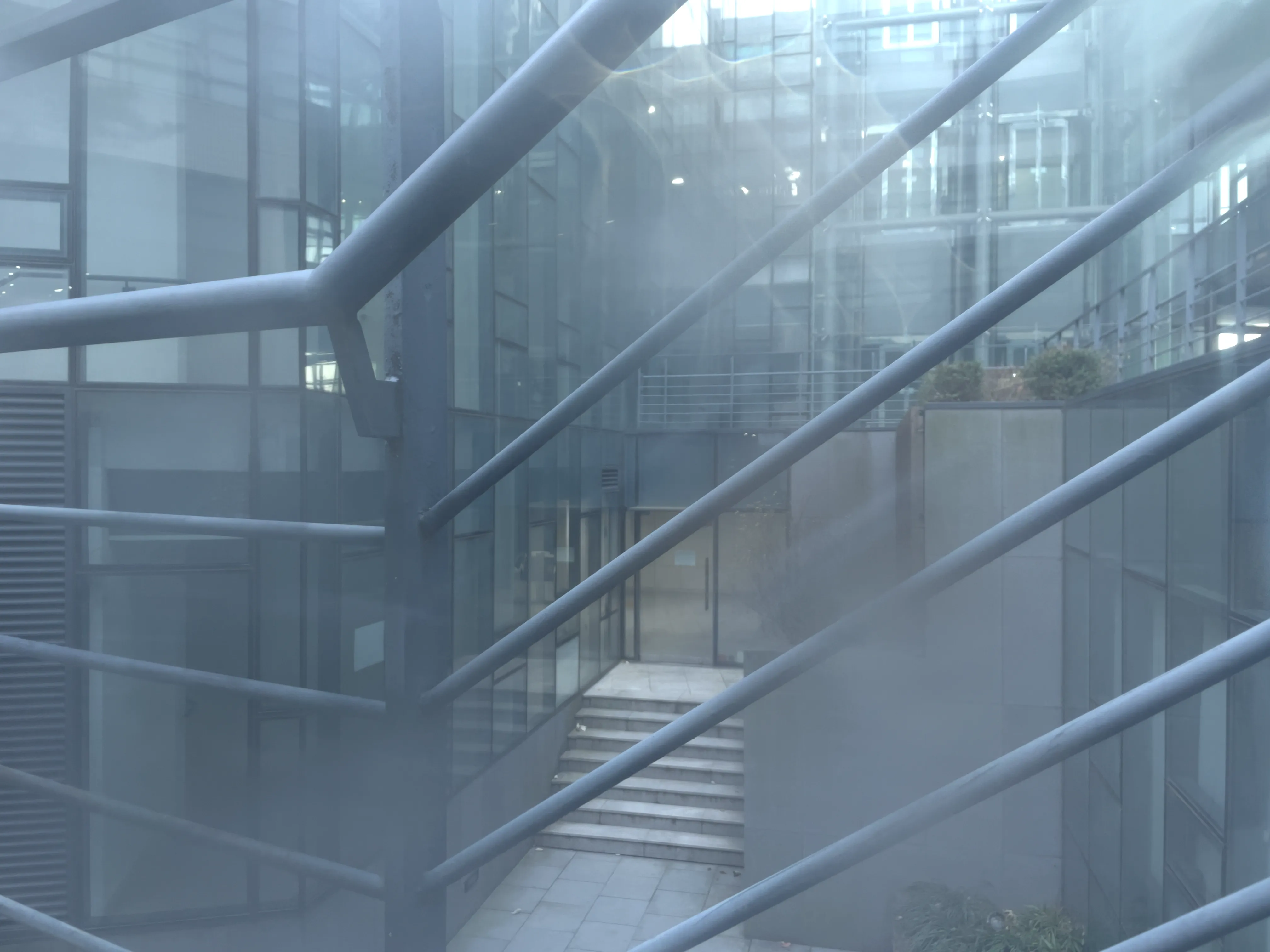
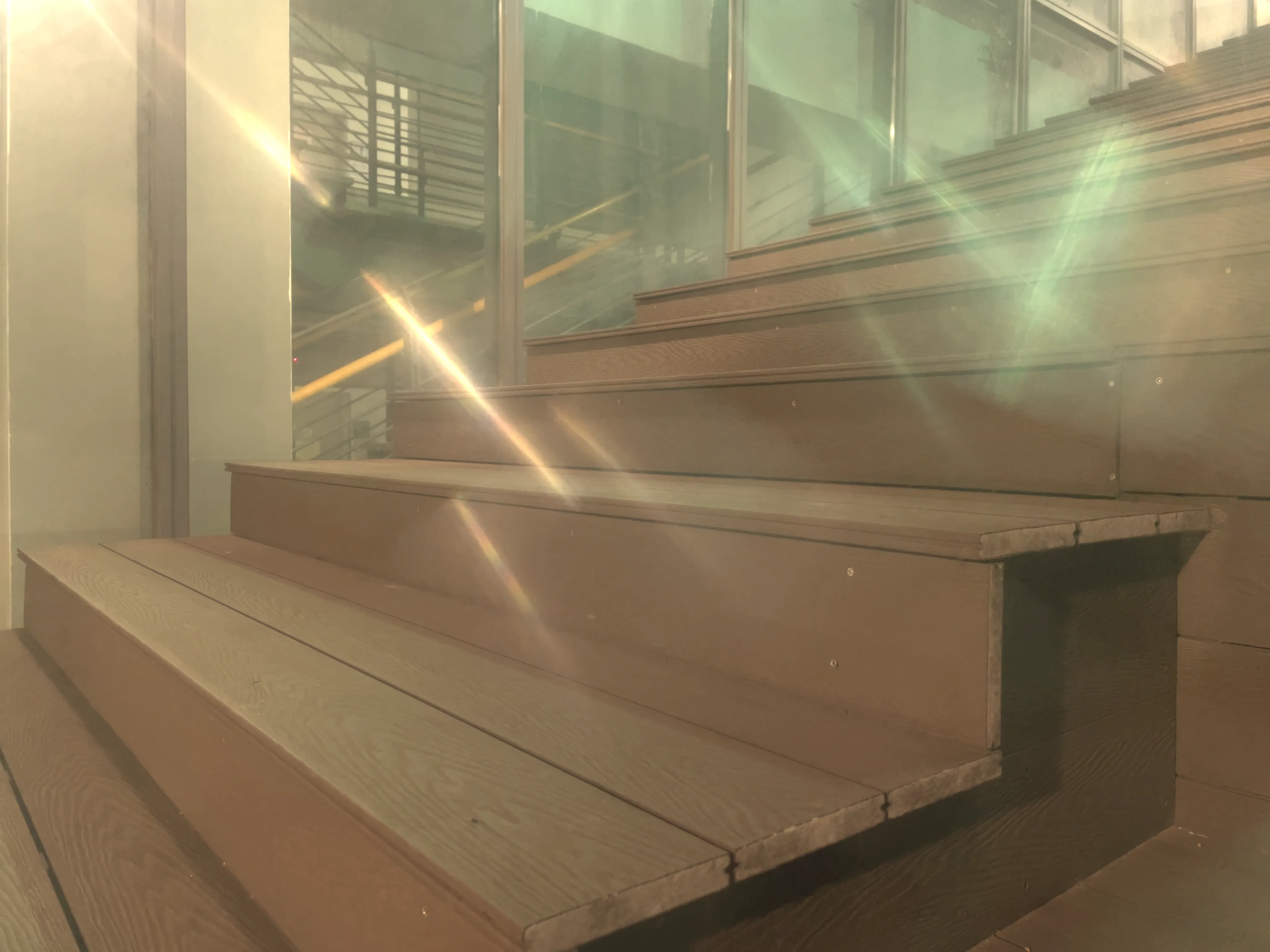
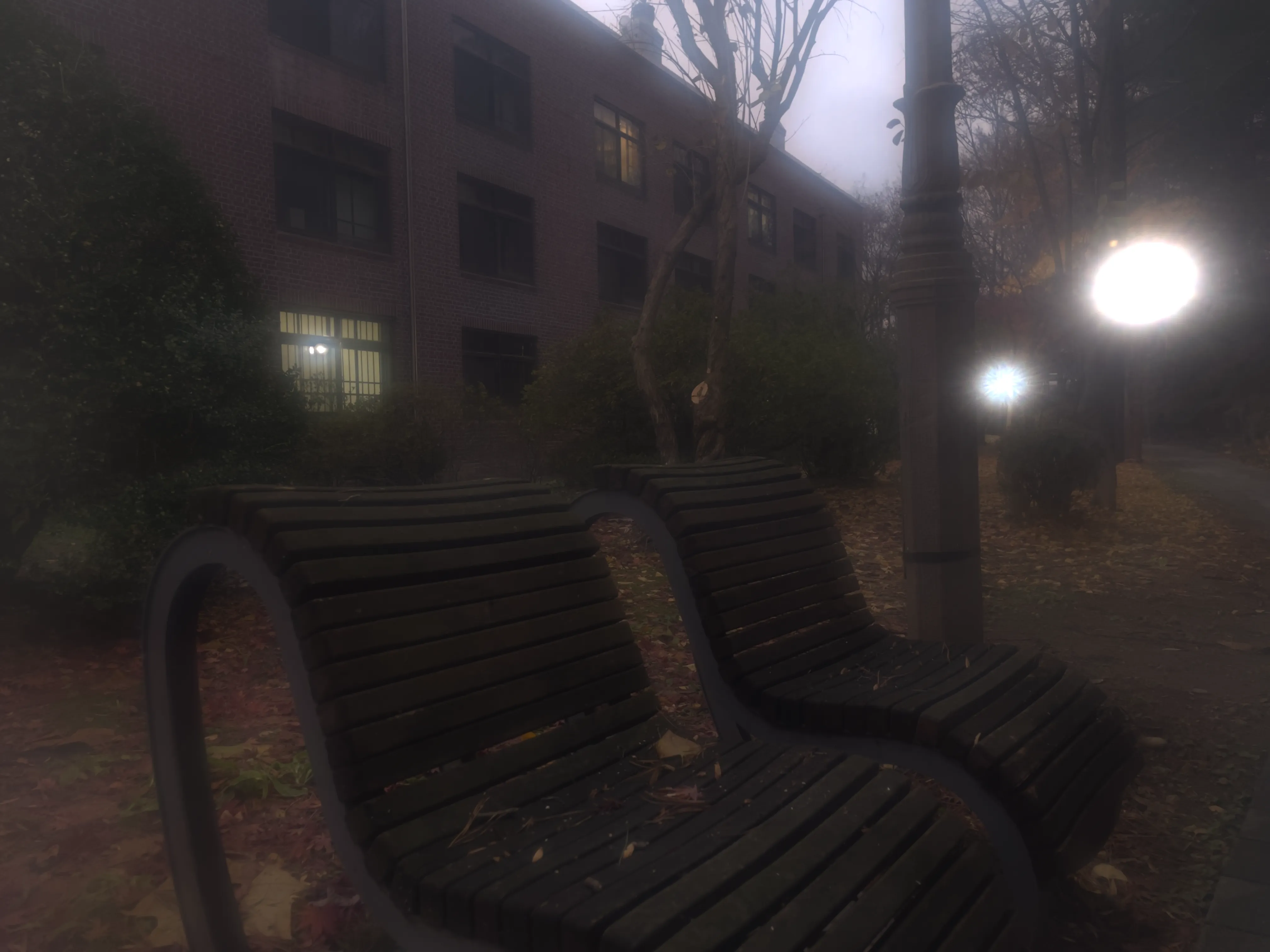
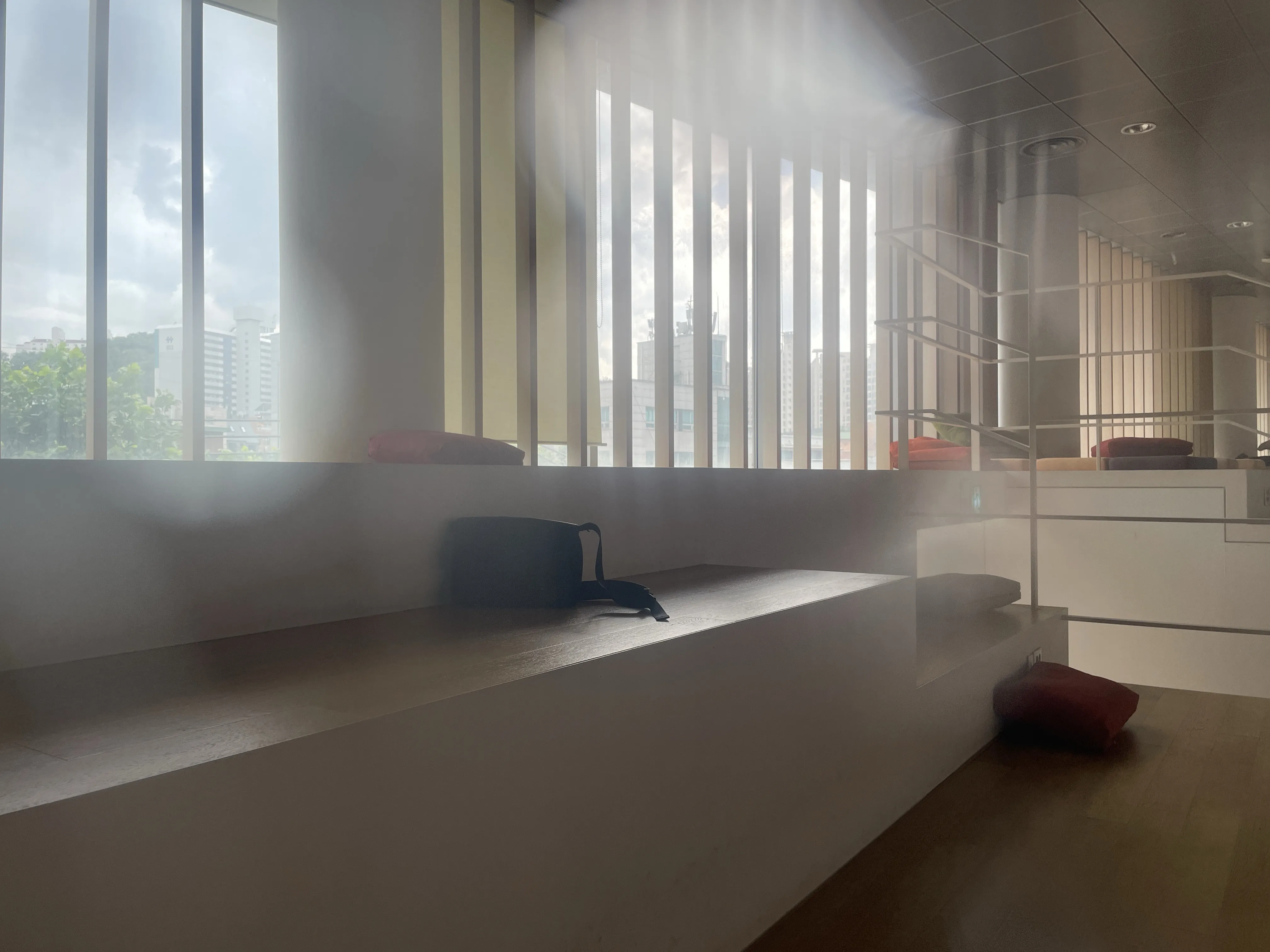
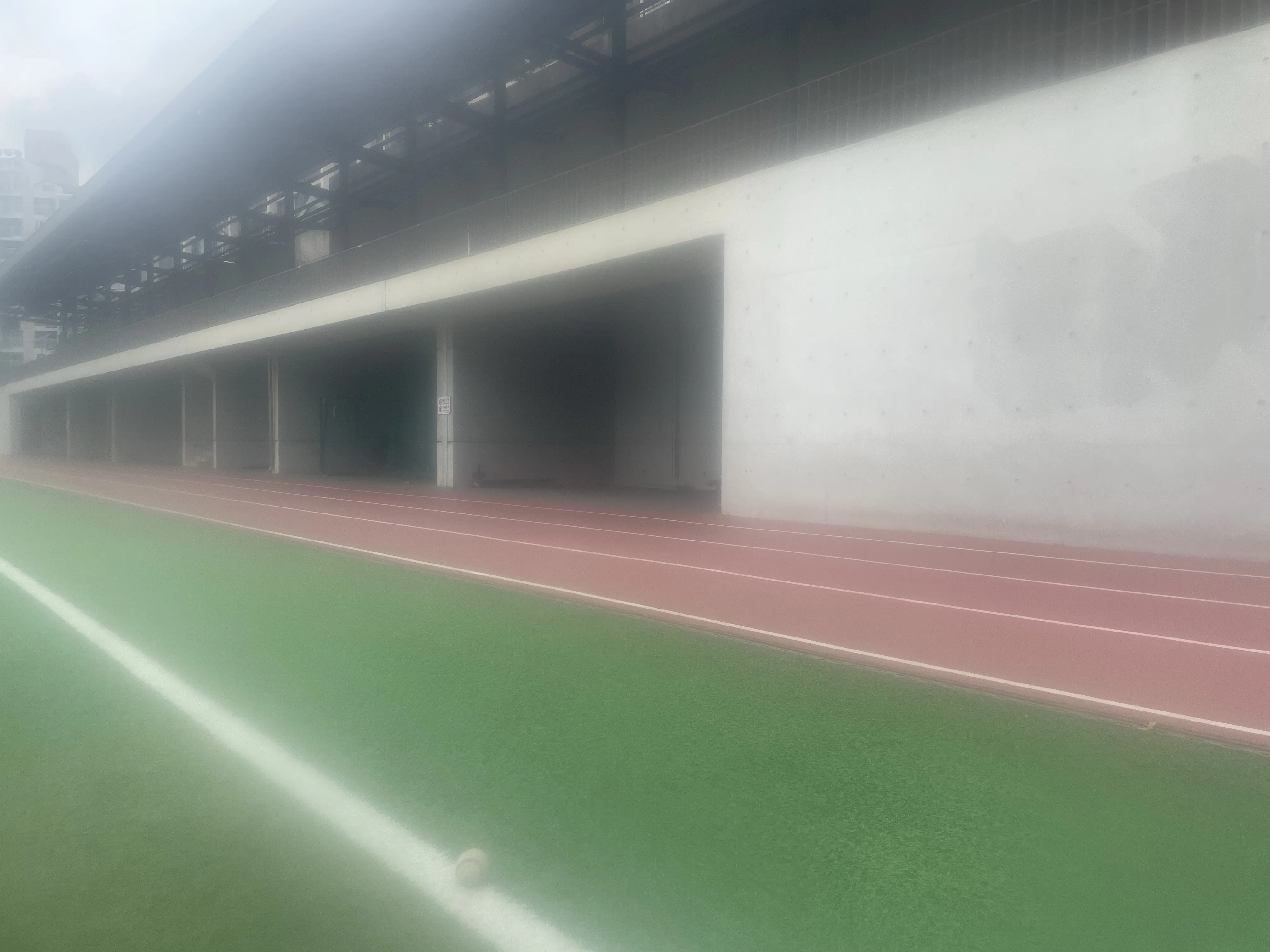
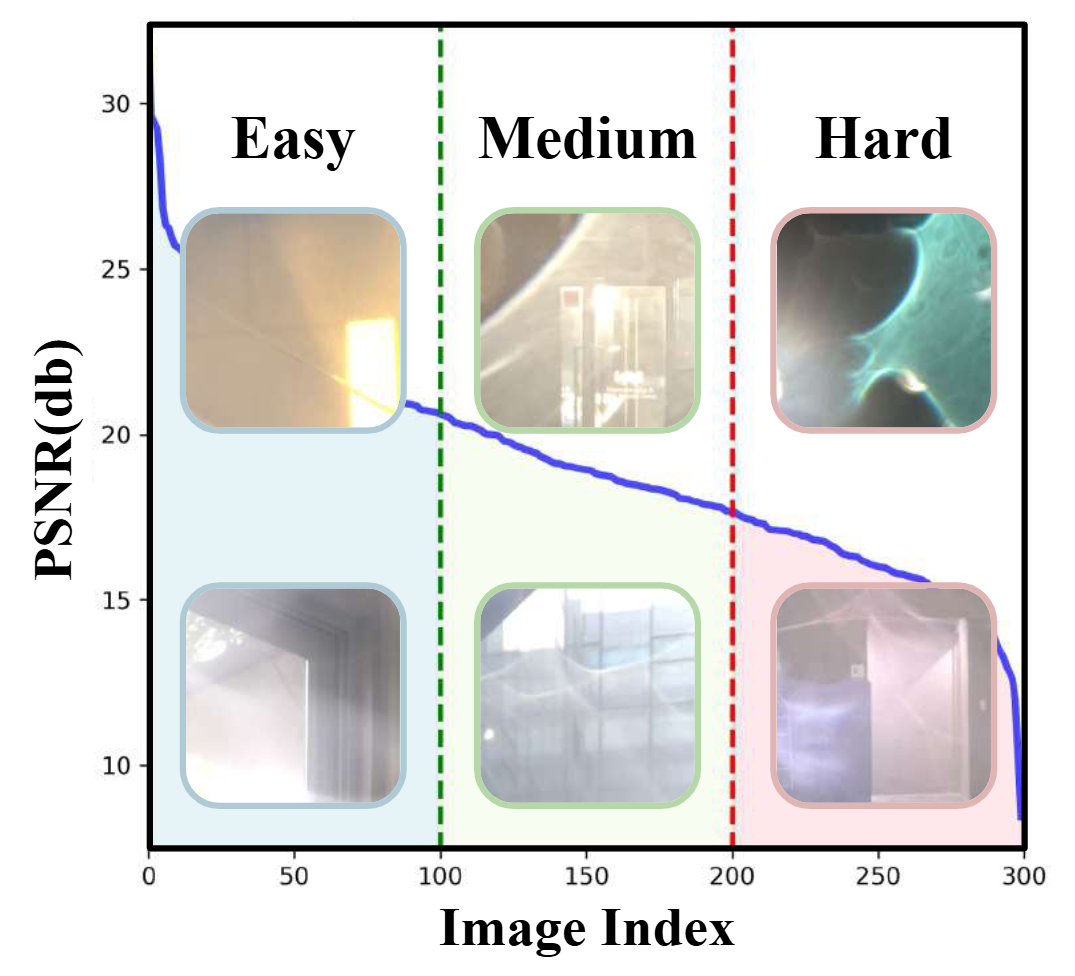
The SIDL benchmark contains 300 static scenes, each captured twice—once without contamination (clean reference) and once through a thin film carrying a controlled deposit. In total, there are 1,588 degraded–clean image pairs at full ProRAW resolution (4032 × 3024, 12-bit DNG). We simulate five real-world contaminant types—fingerprints, dust, scratches, water drops, and mixed debris—applied to the smartphone lens. To allow fine-grained evaluation, we split the degraded images into three difficulty bands based on PSNR between the clean and dirty images: “Easy”, “Medium”, and “Hard”. Scenes span indoor and outdoor settings, day and night lighting, and three levels of artificial illumination. We allocate 240 scenes for training, 20 for validation, and 40 for testing, ensuring each split has balanced coverage of scene types and difficulty levels.
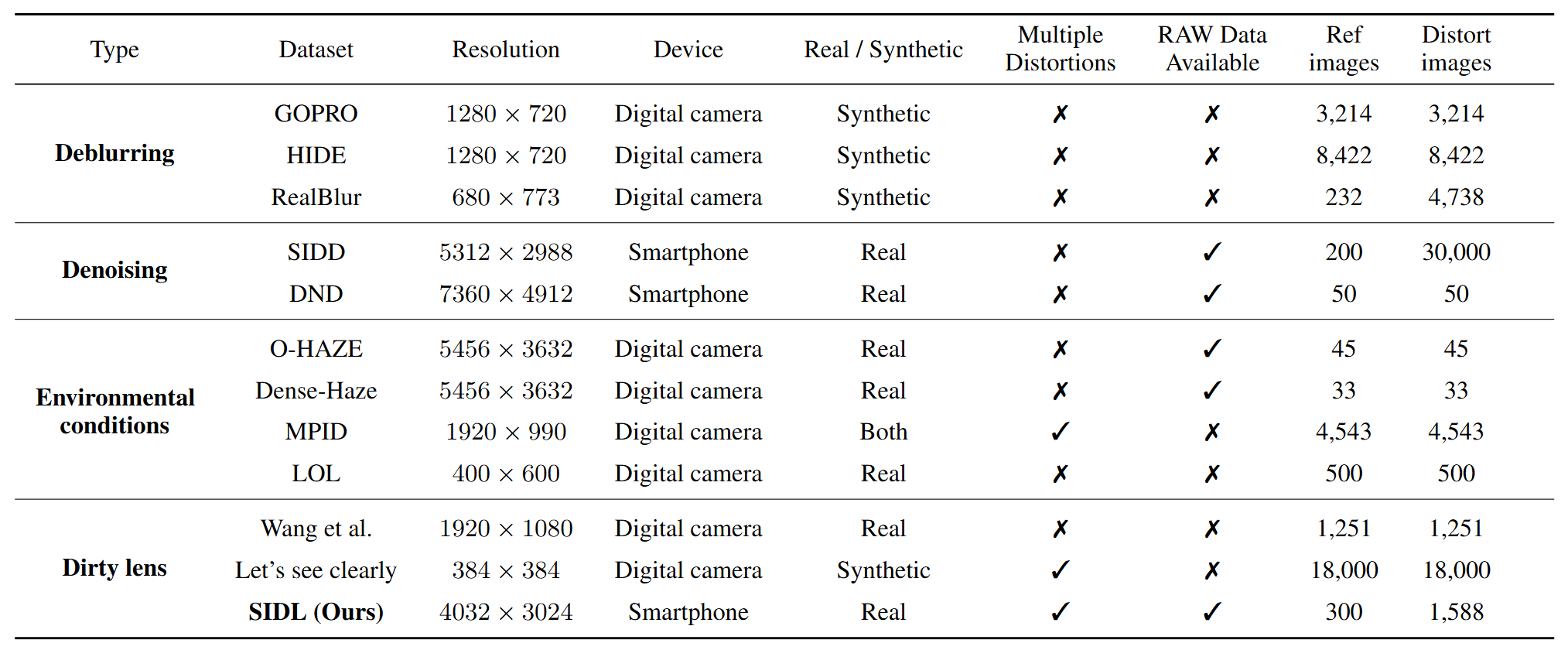
SIDL is unique in offering multiple, real distortion types at smartphone resolution, along with paired RAW data and a large, diverse scene set, unlike previous benchmarks that focus on a single distortion or rely on synthetic noise models.
Image Acquisition
To capture perfectly aligned clean and contaminated images, we designed a 3D-printed film holder that mounts directly in front of an iPhone 12 Pro lens. For each scene, we first shoot a clean baseline, then insert a PVC “dirty film” carrying a precise pattern of water, fingerprint oil, dust particles, scratch marks, or a combination thereof, and shoot the degraded version immediately afterward. This procedure guarantees pixel-level correspondence between each clean–dirty pair, while the film holder allows repeatable, controlled placement of contaminants.

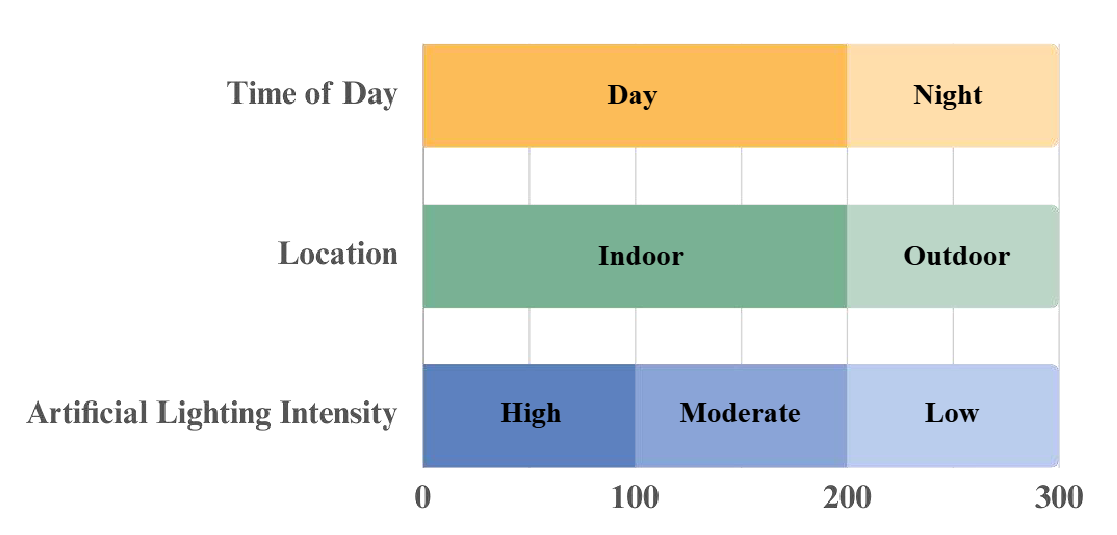
Scene Statistics & Difficulty Distribution
The 300 scenes cover a wide variety of environments:
- Location: indoor labs, offices, outdoor urban and natural scenes
- Time of day: roughly equal splits of day vs. night
- Lighting: three levels of artificial illumination
This diversity ensures that models trained on SIDL generalize across realistic conditions. The PSNR values between clean and degraded images range from as low as 12 dB up to over 30 dB, enabling evaluation under mild to severe contamination. By grouping images into Easy, Medium, and Hard bands, researchers can analyze performance trends as contamination severity increases.
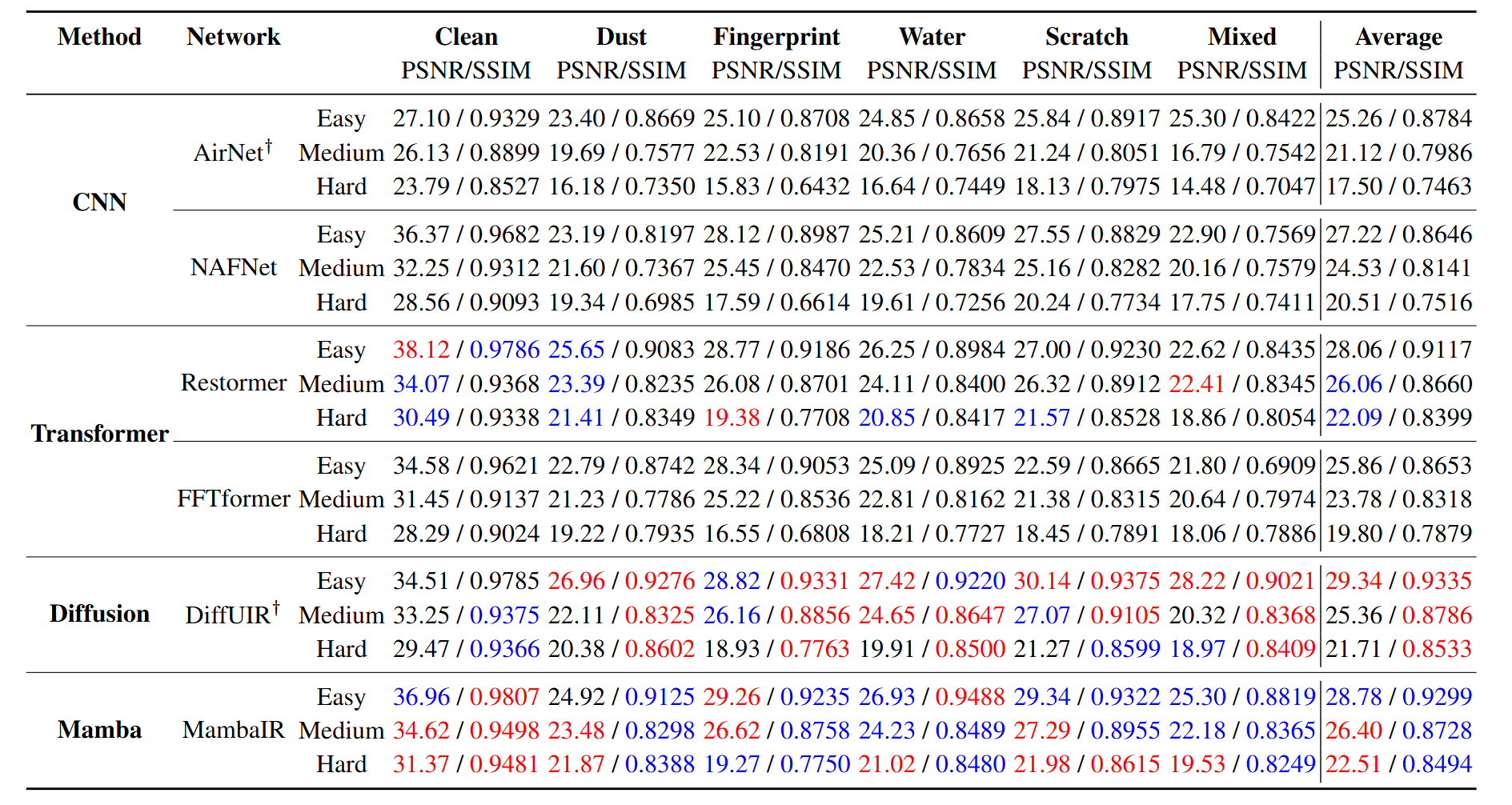
Benchmark Results
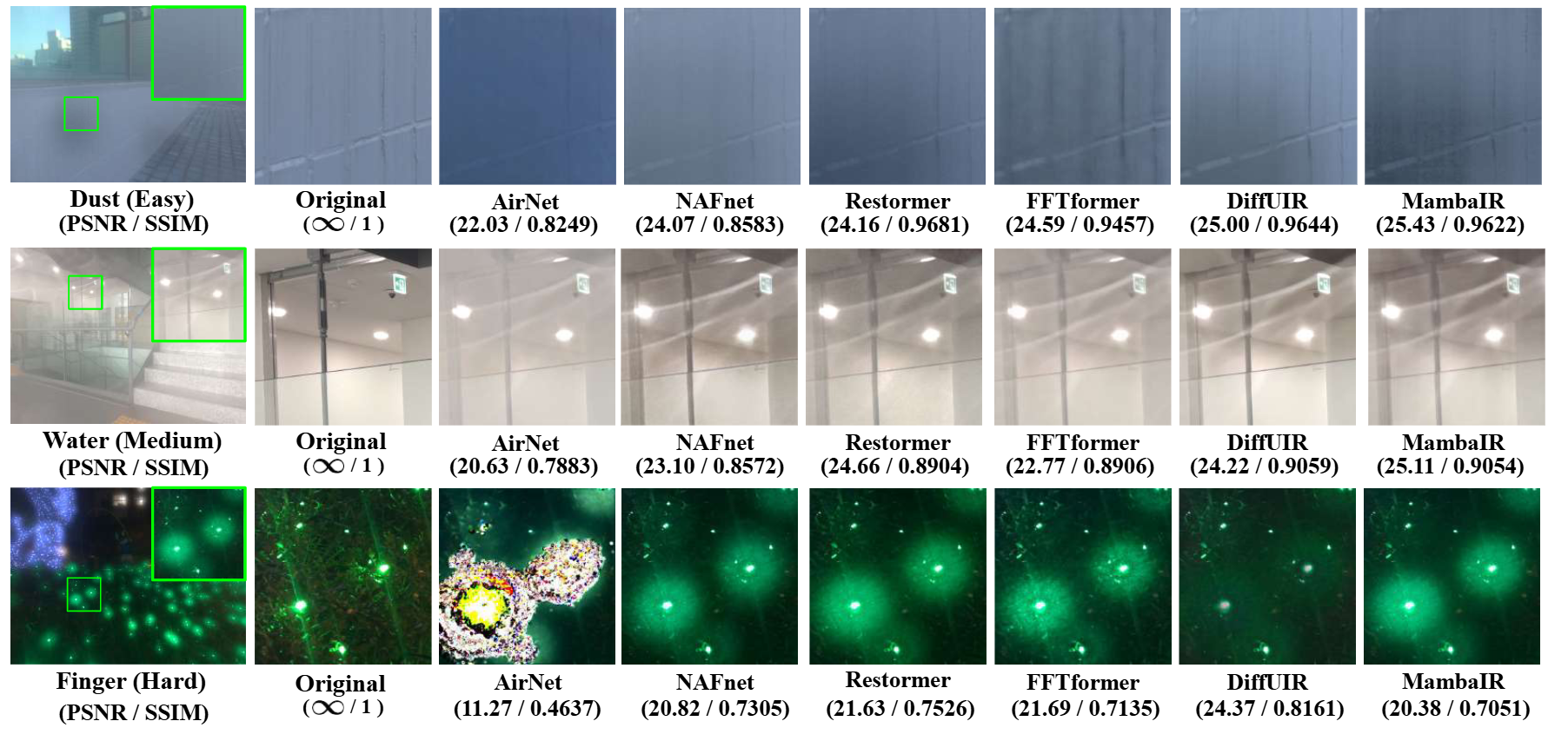
We evaluated six state-of-the-art restoration architectures (AirNet, NAFNet, Restormer, FFTformer, DiffUIR, and MambaIR) on the SIDL test set. While all models improve perceptual quality under mild contamination, their performance drops notably in the Medium and Hard bands. For example, DiffUIR achieves an average PSNR of 26.3 dB on Easy images but only 18.7 dB on Hard images, with SSIM falling from 0.82 to 0.45. Qualitative examples show persistent halos around water droplets and smearing of fingerprint edges under severe conditions, highlighting the challenge of realistic lens contamination.
Download & Evaluation
Patchified Images (512 × 512)
For efficient batch training, download our pre-cropped patches:
Full-Resolution Images (4032 × 3024)
Download the high-resolution images:
RAW DNG & Metadata
Access the original 12-bit DNG files and JSON metadata:
Online Evaluation
Submit your model outputs to our leaderboard server and compare against published baselines:
ISP Pipeline
(to be released)
Citation
@inproceedings{choi2025sidl,
title = {SIDL: A Real-World Dataset for Restoring Smartphone Images with Dirty Lenses},
author = {Choi, Sooyoung and Park, Sungyong and Kim, Heewon},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
volume = {39}, number = {3}, pages = {2545--2554}, year = {2025}
}